
1. General trends in the world economy
|
1. General trends in the world economy 2.1. The CIS and Customs Union 2.7.1. The Republic of South Africa 3. External risks and threats to the economic security of Ukraine |
Now in the world there is a trend of gradual slowdown in the global economy. This is, first of all, due to the following factors:
- weakening of the growth of economies of the EU and developing countries, states of the Asia-Pacific Region and Latin America included;
- a slowdown in China's economic development and the threat of new corporate defaults, which leads to growing of risks to the stability of the financial and banking sector and mining industries of the PRC;
- gradual ending of the US Federal Reserve system's “quantitative easing” program.
Besides, worsening of the geopolitical confrontation between the West and the Russian federation because of the Russian-Ukrainian conflict has led to formation of new financial, economic and geopolitical challenges for global economic development, the main factors of formation of which are as follows:
- spread of negative trends associated with devaluation of the Russian ruble and a significant slowdown in economic development of the Russian Federation, CU and CES member countries, as well as states of Central Asia;
- Moscow's policy of accelerated rapprochement with the PRC (quite possibly up to the level of creation a political and military alliance), which is seen by Washington as a significant threat to its own national interests;
- Moscow's activity to consolidate BRICS' potential in order to accelerate creation of alternative to West's mechanisms for maintaining stable economic development of the association members and oriented to cooperating with it partners from among developing countries;
- growth of the potential for conflict in the political relations between Saudi Arabia and member states of the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf because of Iran issue;
- a significant increase in risks for investors in post-Soviet territories, as well as in regions with high conflict potential due to unresolved territorial disputes (Southeast Asia, South America).
As a result, international specialized agencies have reduced their forecasts for global economic growth in 2014 (Table. 1).
Table 1
Growth forecasts for the world economy in 2014
|
Indexes |
OECD |
IMF |
WB |
EBRD |
|
Previous forecast |
3.6 % |
3.7 % |
3.2 % |
2.7 % |
|
Actual forecast |
3.4 % |
3.4 % |
2.8 % |
1.4 % |
The factors contributing to the development of the world economy today are as follows:
- increased inflation, particularly in the OECD countries where the inflation rate has increased by 2 %, while the annual rate in the G-20 countries – by up to 2.8 %;
- leading by major economies of the West, including the EU, Japan and the UK, a softer monetary policy, while economies of developing countries (India, the RF, South Africa) are taking measures to stabilize income levels;
- the expected increase in the volume of world trade up to 4.7 % this year;
- countries' orientation to the development and implementation of more flexible and adapted to the crisis economic models aimed at stimulation of growth.
- At the same time the growth of the world economy is inhibited by the following factors:
- developed countries' low rates of economic growth which do not allow to ensure stable recovery of the global labor market and raising the number of jobs;
- increase in the trade imbalance of countries of Western Europe, North America and Japan, caused by aging of the population and the high level of unemployment;
- escalation of conflicts in Ukraine, in the Gaza Strip, Iraq and Syria, as well as strengthening of China's territorial claims to Japan, have a negative impact on international markets, investments and prospects for recovery of the global economy;
- introduction of restrictive measures between the Russian Federation and the USA and EU in the bilateral trade and financial sector.
2. Analysis of the development of the world's leading economies and risks around the Russian-Ukrainian conflict
2.1. The CIS and Customs Union
 In the 2nd quarter of 2014 has been observed systematic stabilization of the macro-financial situation in the region. This was preceded by a temporary slowdown in economic growth in the countries of the Customs Union to the level of 1.2 %, caused by a decrease in investment activity in the Russian Federation, weakening of the pace of development in Kazakhstan and low indexes of export-oriented sectors of national economies. Gradual recovery of the budget and foreign trade balance of economies of the region strengthens their resistance to additional risks. At the same time, for the countries with less balanced balance of payments, first of all Belarus, there remains the increased vulnerability to external factors of economic instability. At this, despite the formal removal of customs barriers, Russia continues the practice of economic pressure on its partners (Belarus and Kazakhstan), including raising energy prices and limiting their supplies, as well as closing its market to certain types of Belarusian and Kazakh products.
In the 2nd quarter of 2014 has been observed systematic stabilization of the macro-financial situation in the region. This was preceded by a temporary slowdown in economic growth in the countries of the Customs Union to the level of 1.2 %, caused by a decrease in investment activity in the Russian Federation, weakening of the pace of development in Kazakhstan and low indexes of export-oriented sectors of national economies. Gradual recovery of the budget and foreign trade balance of economies of the region strengthens their resistance to additional risks. At the same time, for the countries with less balanced balance of payments, first of all Belarus, there remains the increased vulnerability to external factors of economic instability. At this, despite the formal removal of customs barriers, Russia continues the practice of economic pressure on its partners (Belarus and Kazakhstan), including raising energy prices and limiting their supplies, as well as closing its market to certain types of Belarusian and Kazakh products.
Central Asian states since the beginning of the Russian-Ukrainian conflict have been taking a reserved position, not condemning officially the steps of the Russian Federation against Ukraine, on the one hand, and not recognizing the results of the referendum in the Crimean and annexation of the Peninsular by Russia - on the other hand. At the same time, these countries are already experiencing discomfort and consequences of the crisis in relations between Russia and Ukraine in the economic sphere.
2.1.1. The Russian Federation
Current trends of development. Strengthening in the Russian economy of strongly negative trends due to the effect of sanctions of first and second level imposed by Western countries. Problems in the economy significantly impede the Russian government to provide effective strategic planning and management of socio-economic processes in the state.
According to the results of the 1st half of 2014, in the Russian economy have got shaped the following negative trends:
- slowdown (1st quarter – 0.9 %, 2nd quarter - 0.8%) of the economic growth rate to the level of balancing on the edge of technical recession with weakening of investment activity and decrease in the rate of growth of real incomes of the population;
- low effectiveness of the Government's steps to reduce the deficit of regional budgets (with the prospect of increasing the corresponding figure for the consolidated results of the year to 700-800 billion rubles, in 2013 - 640 billion rubles) due to a slowdown in economic growth rate. At this, the volume of the public debt of subjects of the Russian Federation as compared to the first half of 2013 has increased by 23.8 % (to 1.742 billion rubles);
- weak effectiveness of the Russian authorities' measures aimed at stimulation of the economy by monetary methods due to a combination of the lowest unemployment (4.9 %) with high inflation (7.8 %). There is a slowdown and deteriorating of credit conditions and, consequently, higher interest rates and lower consumer confidence of the population;
- reduction since the beginning of the year of the volume of international reserves of the Central Bank of Russia by 31.3 billion US dollars (as of July 1, 2014 they were 478.25 billion US dollars) in combination with the outflow of foreign capital (about 80 billion US dollars since the beginning of the year) has significantly narrowed the investment opportunities of the Russian Federation, led to continued instability in industrial production and construction. It has also forced the Russian government to seek additional sources of funding for programs of import substitution.
So, under the influence of sanctions of the first and second levels, the minimum amount of direct and indirect losses of the Russian side has already reached more than 130 billion US dollars, and by the results of this year, the outflow of capital from the RF could exceed 200 billion US dollars. Besides, a key source of growth in Russia's GDP is almost exclusively net exports, which significantly increases vulnerability of the Russian economy from the adverse (in the context of the situation) development of the situation on the world oil market. At this, oil and gas revenues will be used by the government to compensate for the shortfall of income from other sectors of the economy.
 Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. Taking into consideration that the US and EU sector sanctions are mainly focused on generating effect in the medium term (up to 3 years), in 2014-2015 the greatest risks for the Russian economy will be restrictions regarding the financial sector of the Russian Federation. The need to replace external borrowing will encourage Russian authorities to use for this part of the oil and gas revenues (NWF), which will entail a significant reduction in the volume of new revenues to the Reserve Fund.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. Taking into consideration that the US and EU sector sanctions are mainly focused on generating effect in the medium term (up to 3 years), in 2014-2015 the greatest risks for the Russian economy will be restrictions regarding the financial sector of the Russian Federation. The need to replace external borrowing will encourage Russian authorities to use for this part of the oil and gas revenues (NWF), which will entail a significant reduction in the volume of new revenues to the Reserve Fund.
Limitation of the access to foreign capital markets for Russian banks and companies that have come to sanctions lists can cause:
- additional acceleration of inflation at the level of 0.7-1 % (annualized) due to the need to provide assistance to banks to support liquidity (excluding the “Savings Bank” VTB, “Gazprombank”, VEB, “Bank of Moscow” and “Rosselkhozbank”'s paying during 2014-2015 of the external debt on existing obligations which amounts to 66 billion US dollars);
- decrease in profitability of the banking sphere due to the expected reduction by these banks of the volume of private and corporate lending, may cause a slowdown in the dynamics of the development of this sector of the Russian economy (negative effect is estimated at the level of 0.5 % of GDP);
- decrease in retail sales with the reduction of household consumption (negative effect is estimated at 0.2 % of GDP).
Despite the fact that the USA and EU's sanctions against Russia in the fuel and energy sphere will not have tangible negative consequences for Moscow in the nearest future (the greatest risks arise for “Rosneft”, which in December 2014 and February 2015 must has to repay 26.5 billion US dollars loan obtained for the acquisition of TNK), however:
-
 is expected suspension of the Arctic shelf development, reducing the number of proposals of foreign companies within the framework of new projects for cooperation in the development of inaccessible areas, decline in energy production due to the use of obsolete technologies and focusing on production of energy carriers from old fields;
is expected suspension of the Arctic shelf development, reducing the number of proposals of foreign companies within the framework of new projects for cooperation in the development of inaccessible areas, decline in energy production due to the use of obsolete technologies and focusing on production of energy carriers from old fields; - long period of sanctions and their gradual expansion may cause a reduction in Russian oil production in volumes up to 10-20 million tons per year, which threatens the Kremlin with losing the most sustainable source of funding for priority state projects and programs.
Western countries' restrictions on the Russian Federation's supplies of dual-use products, as well as an embargo on trade in arms and military technologies will directly constrain the pace of the Kremlin's implementation of national programs to reduce dependence on imports of the Russian military-industrial complex, rocket building, aircraft building, shipbuilding and atomic-industrial complex.
Forecast. By results of 2014 the potential for economic growth of Russia is estimated at 0.2-0.5 % with the prospect of worsening of this forecast in case of further strengthening of the economic pressure from the West. Already in 2015, Russia may face problems of sustainable deficit of financial resources, accelerated depreciation of fixed assets, gradual degradation of infrastructure and main communications.
Against the background of the above-mentioned complex of negative processes in the Russian economy, as of July 2014 a key task of the Russian government was preventing the reduction of the real income of the federal budget. Russia should also provide support to industries which ensure the growth of industrial production, the sector of financial and banking services and retail trade in order to prevent further economic slowdown due to negative consumer expectations of the population. Of particular importance is the issue of long-term sustainability of funding sources for most priority programs of import substitution and implementation of powerful infrastructure projects, in the occupied Crimea included.
At the same time, in relation to Ukraine, Russia will continue realizing the scenario for disruption of the implementation of the anti-crisis program for stabilizing the financial and economic situation in Ukraine with a view to its further transformation into a scenario for destruction of the existing foundations of Ukrainian industry and, eventually, of the economy.
2.2. The USA
 Current trends of development. Taking measures to strengthen mechanisms to accelerate economic growth remains the top USA's priority. After a significant reduction in comparison with the 1st quarter of 2014, US GDP growth for the second quarter of 2014 was 4 %, while the GDP in the same period of 2013 - 2.4 %. We can also see acceleration of inflation, increase in the volumes of lending to the private sector and industrial production, recovery of economic capacity, improvement of the situation in the labor market (the unemployment rate is 6.2 %).
Current trends of development. Taking measures to strengthen mechanisms to accelerate economic growth remains the top USA's priority. After a significant reduction in comparison with the 1st quarter of 2014, US GDP growth for the second quarter of 2014 was 4 %, while the GDP in the same period of 2013 - 2.4 %. We can also see acceleration of inflation, increase in the volumes of lending to the private sector and industrial production, recovery of economic capacity, improvement of the situation in the labor market (the unemployment rate is 6.2 %).
At this, the United States plans to maintain a flexible monetary policy in the current situation, and the question of the beginning of rising interest rates remains open. Against the background of increasing investors' expectations for the US Federal Reserve System's raising interest rates and the deterioration of the situation in the EU, the dollar is getting stronger. However, the uneven recovery of the growth rate of the US economy against the background of deepening of the Russian-Ukrainian crisis, which generates additional challenges for the global economy, restrains the FRS from raising interest rates, leaving this tool of stimulation of the economy as insurance against stagnation processes.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. The USA's position is absolute non-recognition of the Russian Federation's occupation of the Crimea, taking measures for gradual isolation of the Russian Federation, providing Ukraine with broad political, diplomatic, financial and informational support, while refraining from military and military-technical assistance. The Russian Federation's aggression against Ukraine, its sovereignty and territorial integrity, is seen by the USA as a violation by Moscow of basic norms of international law that threatens international peace and security.
In July 2014 the United States announced about imposing sectoral sanctions against the Russian Federation, the most important of which is to limit the access of Russian companies and financial institutions to Western financial markets. The USA's potential economic losses from Moscow's retaliatory sanctions (food embargo) are estimated at 1-1.5 billion US dollars and are well below the expected losses of the EU.
Taking this into account, experts forecast increased pressure on Washington from the European Union to speed up the development of joint steps to counter Russian countermeasures. This, first of all, will include the need to better take into consideration the official position of Brussels within the framework of negotiations on creation of the so–called “Transatlantic Free Trade Area”.
Forecast. Despite the positive trends in the economy of the USA, the forecast for economic growth this year has been revised downwards to the level of 2-2.3% for the year. Besides, in the nearest future no significant positive changes are expected in the labor market and in the inflation indicators. Despite the official Washington's forced shifting of the geopolitical focus of attention from the Asia-Pacific region to the European continent as a result of the Russian aggression against Ukraine, unconditional strategic priority of the United States will continue to be the policy of containment of China. Given this, the United States will have to carry out diplomatically and economically costly policy aimed at strengthening of the international isolation of the Russian Federation, on the one hand, and counteracting China's strengthening - on the other.
2.3. European Union
 Current trends of development. At present, there are all the signs of a slowdown in the rates of development of the European economy (GDP growth in the II quarter of 2014 made 0.7 %) — decline in industrial production in countries of Euro-zone, including France (-2 %) and Greece (-6.7%), reduction of the trade surplus of the currency bloc to 16.8 billion Euros (in June 2014), decrease in the index of business activity in the EU countries. The positive effect of taken in June by the European Central Bank stimulus steps, including reduction of the basic interest rate to 0.15 % per annum and the beginning of the target program of lending banks will only be seen over time.
Current trends of development. At present, there are all the signs of a slowdown in the rates of development of the European economy (GDP growth in the II quarter of 2014 made 0.7 %) — decline in industrial production in countries of Euro-zone, including France (-2 %) and Greece (-6.7%), reduction of the trade surplus of the currency bloc to 16.8 billion Euros (in June 2014), decrease in the index of business activity in the EU countries. The positive effect of taken in June by the European Central Bank stimulus steps, including reduction of the basic interest rate to 0.15 % per annum and the beginning of the target program of lending banks will only be seen over time.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict.
As a result of the EU's imposing sectoral sanctions of the third level against the Russian Federation and the Russian response, the total economic losses of the EU countries may reach 40 billion Euros (0.3 % of EU GDP). At this, the greatest losses from the introduction of Russian embargo on food imports from the EU, have suffered Poland (1.1 billion US dollars in 2014), Germany (814 million US dollars), the Netherlands (797 million US dollars), Spain (796 million US dollars), Denmark (545 million US dollars), France (444 million US dollars), Finland (367 million US dollars). However, the total of losses of the largest economies of the European Union (Germany, UK, France, Italy, and Spain) in relation to the overall indexes of their exports is negligible in comparison with Poland or Finland.
Taking into consideration the above-mentioned, the main risks to the EU from Russia's ban on imports of European food products are as follows:
- slowdown of economic growth (economic recovery) of individual countries of Eastern, Southern and Northern Europe (especially Poland, Lithuania, Greece, Finland), agro-export of which was mainly focused on the Russian domestic market. At the same time the EU losses from reduced food exports to the Russian Federation because of the embargo, can be up to 25 % of the total annual supply of agro and food products, which are estimated at 12 billion Euros (potential losses — 3 billion Euros). Despite this, the Russian side estimates the EU's potential losses much higher;
- growth of the level of unemployment and allocation of additional funds for social programs. This is due to the prospect of new complications in the labor market caused by lower domestic prices in the European food market, which could trigger a wave of bankruptcies of small farms;
- possible strengthening of sanction pressure on the EU in case of the spread of Russia's ban on imports of alcoholic beverages and baby food.
At the same time, the risks to the economy of the EU in the context of the Russian aggression against Ukraine are estimated as significant. Taking this into account, the EU seeks to ensure balanced decisions on economic sanctions against Russia, preferring hidden financial sanctions.
Forecast. Systemic risks to the economy of the European Union remain a high debt burden, problems in the banking sector, poor domestic demand, high unemployment, and incomplete adjustment of existing imbalances of economic development (in 14 EU member states has been applied the procedure of excessive budget deficit).
2.3.1. Germany
Current trends of development. The high activity of the business environment, positive trend in the labor market, moderate inflation and favorable indicator of consumer moods ensure the German economy's being in the process of recovery. In this context, certain slowdown in GDP growth in the 2nd quarter of 2014 (0.8 %) is not considered as critical. At the same time Germany is threatened by the European Commission's possible application of sanctions for the excessive foreign trade proficit.
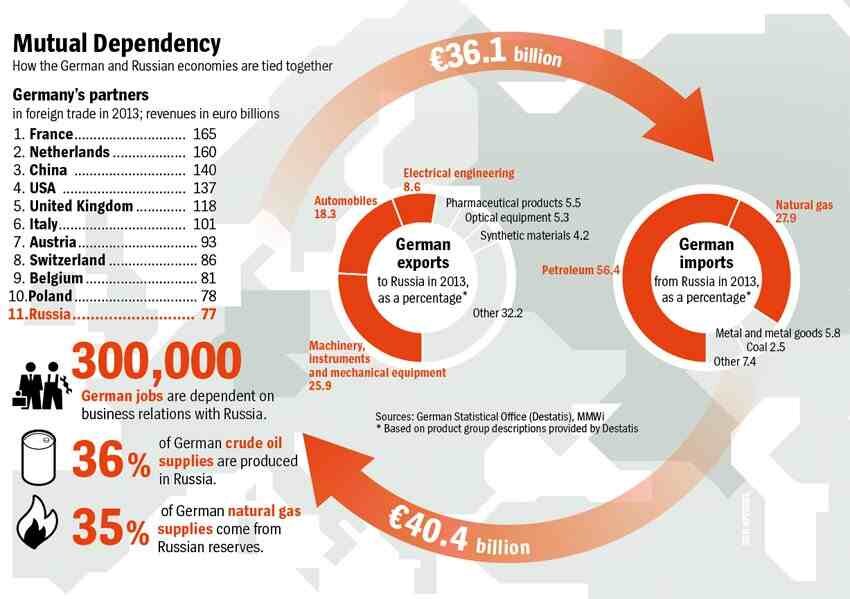 Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. The leadership of Germany within the framework of settlement of the Russian-Ukrainian crisis comes exclusively from ensuring its own national interests. Berlin's cautious approaches to radical enhance of the economic pressure on the Kremlin are caused by:
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. The leadership of Germany within the framework of settlement of the Russian-Ukrainian crisis comes exclusively from ensuring its own national interests. Berlin's cautious approaches to radical enhance of the economic pressure on the Kremlin are caused by:
- high dependence of the economy of Germany on Russian hydrocarbons (share of oil imports from the RF is 56.5 %, of gas - about 30 %);
- significant losses that have been incurred by German companies operating in the Russian Federation;
- close trade and economic ties (in 2013 bilateral trade amounted to 76 billion Euros) and serious social consequences (about 300 thousand workers are engaged in cooperative relations with the Russian Federation).
Actions that are carried out by the German side for the economic pressure to coerce the Russian side to de-escalate the situation in the East of Ukraine, are much less than Berlin's potential. The introduced (within the framework of the EU's sectoral sanctions) restrictions on cooperation with the RF, will only slightly affect the German economy, and losses of exporters will be compensated by the government through providing them with additional support to enter the alternative markets. However, in case of Russia's entry into the phase of rapid economic decline or Moscow's taking measures for limitation of oil and gas supplies to the EU, negative effects will be especially felt by German manufacturers of railway transport (11 % of German exports to Russia), industrial equipment (6 %), mechanical engineers (5 %), car manufacturers (4 %), electrical engineers (3 %), chemical and pharmaceutical products (3 %), air transport (2 %).
The official Moscow's ban on imports of certain food products from the EU is not considered by the official Berlin as an important threat to the economic interests of Germany. However, the declared by the Russian side preparing of the so-called “second package” of sanctions against the United States and the European Union (most likely, will primarily include restrictions on the supply of a separate list of machinery and equipment which Russia is able to replace with its own counterparts) can cause more significant damage to German producers and exporters of industrial products and related services.
With this in mind, the official Berlin makes every diplomatic effort to achieve (until the end of October) progress in de-escalation of the situation in the East of Ukraine, which will allow the German side to avoid build-up of conflict in relations with Moscow.
Forecast. Despite some deceleration of economic development in Germany in the 2nd quarter, the government forecast for further growth of GDP at the end of 2014 remains at 1.5 %. The main directions of A. Merkel's Government's efforts are to attract investments into development of infrastructure, to accelerate the process of transition of the energy sector to renewable energy sources, pension reform. At this, as a result of low unemployment and high domestic demand, there is a possibility of acceleration of the economy of Germany in the absence of further steps to strengthen the economic isolation of the Russian Federation.
2.3.2. Great Britain
 Current trends of development. Favorable trends in the economic development of Great Britain in the 2nd quarter of 2014 (stable GDP growth at 3.2 %, a decline in the unemployment rate to 6.4 %, no risk of deflation) are facilitated by David Cameron's Government's sticking to the clear course to fiscal consolidation. However, the development of the British economy is threatened by the increasing cost of housing and the low level of industrial production growth (1.2 % as of July). These factors can lead to a recession. However, the biggest concern in financial and industrial circles over the last time is about the development of the situation around the preparations for the parliamentary elections in 2015.
Current trends of development. Favorable trends in the economic development of Great Britain in the 2nd quarter of 2014 (stable GDP growth at 3.2 %, a decline in the unemployment rate to 6.4 %, no risk of deflation) are facilitated by David Cameron's Government's sticking to the clear course to fiscal consolidation. However, the development of the British economy is threatened by the increasing cost of housing and the low level of industrial production growth (1.2 % as of July). These factors can lead to a recession. However, the biggest concern in financial and industrial circles over the last time is about the development of the situation around the preparations for the parliamentary elections in 2015.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. At present, the conflict over Ukraine mainly increases the risks primarily for British companies operating in the RF and having business interests in the Russian energy sector. Thus, the EU's introduction of restrictions on exports to Russia of equipment and technologies related to energy engineering (export licenses will not be issued for products intended for the extraction and production of deep-sea oil, exploration or extraction of Arctic oil and shale oil projects in the Russian Federation), may cause losses to such companies with British capital as “Shell” (involved in the project “Sakhalin-2”) and “British Petroleum” (has signed an agreement to establish a joint venture with the Russian side in the search and development of shale oil in the Volga-Ural region). Also, losses may be incurred by such powerful companies as “Marks & Spencer” (a chain of stores in Russia), “Rolls-Royce” (supplies RF aircraft engines), “Diageo” (alcoholic beverages), “Intercontinental” (Hotel business).
It is expected that increased economic pressure on the Russian Federation could lead to a reduction in the total volume of foreign investments into the United Kingdom at the expense of decrease of the “Russian share” (due to freezing of assets of the oligarchs, the outflow of Russian financial resources to other international financial centers), as well as provoke a crisis on the capital real estate market.
At the same time, despite the strong political support of Ukraine, the UK Treasury has denied the European Commission in its proposal to increase the EU member states contributions to cover the costs of a program of economic assistance to Ukraine (the estimated growth of the volume of aid was to be 500 million pounds). Thus, at this stage, the British political circles are ready to go only to certain economic costs, partially shifting the burden of sanctions onto the most powerful industrial companies that have ample opportunity to diversify their investment portfolios.
Forecast. In July, the IMF improved the forecast of growth of the British economy in 2014 - from 2.8 % to 3.2 % because of the positive dynamics of key macroeconomic indicators and the adoption of effective anti-crisis measures in the country at this stage.
2.3.3. France
 Current trends of development. The main catalysts of deepening of the crisis in the economy of France have become unstable macroeconomic indicators in the 2nd quarter of 2014 (GDP rose by only 0.3 %, balance of visible trade was negative at 5.3 billion Euros, reduction in industrial production made 2 %). This once again actualized to the President of France the question of rotations in the economic bloc of M. Waltz' Government (by resignation of the Cabinet of Ministers at the end of August 2014).
Current trends of development. The main catalysts of deepening of the crisis in the economy of France have become unstable macroeconomic indicators in the 2nd quarter of 2014 (GDP rose by only 0.3 %, balance of visible trade was negative at 5.3 billion Euros, reduction in industrial production made 2 %). This once again actualized to the President of France the question of rotations in the economic bloc of M. Waltz' Government (by resignation of the Cabinet of Ministers at the end of August 2014).
In order to reduce the budget deficit (on request of the European Commission), the government sold the state share unit in the energy company “GDF Suez” (in the amount of 1.5 billion Euros) adopted a program of additional budget cuts (4 billion Euros), and also introduced tax credits for low-income population strata. As part of fulfillment of its election campaign promises, authorities plan to introduce in autumn the second program of assistance to grassroots territorial-administrative units with the most serious economic imbalances (5 billion Euros).
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. France is the third largest foreign investor into the Russian Federation's economy (more than 1.2 thousand French companies are working directly in Russia). Due to the strengthening by the European Union of sanctions against the Russian Federation, in the country are observed the following trends:
- reduction of the profitability of French food exports, given that Russia accounts for 8 % of the total supply in this sphere (about 6 thousand French firms regularly export agricultural and agro-food products to the Russian market);
- French companies have begun to revise their relations with Russian partners. For example, oil and gas concern “Total” has suspended the purchase of shares in the Russian company “Novatek”; company “EDF Trading” has abandoned Russian thermal coal, which was supplied by the coal company “Zarechnaya”;
- a high risk for financial and banking sector of France due to the strong presence of the French capital in the banking sector of Russia (Russian customers have taken loans amounting to 36.5 billion Euros).
In case of strengthening of economic sanctions against the Kremlin, the greatest losses may suffer such companies as “Societe Generale”, “Alstom”, “Renault”, “Peugeot”, “Citroen”, “L'Oreal”, “Auchan”, “Leroy Merlin”, “Decathlon”, “Accor”, “Vinci Construction”, “Air Liquide”, “Alcatel-Lucent”, “Areva”, “Essilor”.
Forecast. The leadership of France commits itself to the course of easing the monetary policy and parallel search of funds to fulfill its election campaign promises to improve living standards of the population. There is growing the threat of further preservation in the country of the unemployment rate at 10 % due to the deterioration of the rate of development of companies connected with Russian and Ukrainian markets. According to preliminary estimates, the annual GDP growth rate in 2014 will amount to 0.5-0.6 %.
2.3.4. Italy
Current trends of development. The macroeconomic situation in Italy is in the stage of technical recession. The decline in GDP has been observed during the second quarter in a row (by 0.3 % in the 2nd quarter of 2014), and the level of public debt has reached 96 billion Euros (up by 4.7 % since the beginning of the year). In order to fill the revenue side of the budget, since July 1 one has been raised the tax rate on financial income - from 20 % to 26 % (an additional measure to fill the budget and stimulate the activation of the stock market). For September 2014, is scheduled the beginning of an ambitious reform program. In particular, among urgent measures are as follows: 9 months to provide tax incentives to businesses that buy new equipment; to allow insurance funds to lend to companies; to reduce electricity tariffs for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. Italy has the status of one of the biggest trade partners of the Russian Federation (inferior only to China, the Netherlands and Germany), having a wide range of bilateral cooperation in spheres such as energy engineering (Italian companies are involved in construction of the gas pipeline “South Stream”, the development of the shelf of the Black Sea and the Barents Sea, gas fields on the Yamal Peninsula; “Lukoil” and “Rosneft” carry out oil refining in Sicily and Sardinia; “Gazprom Neft” produces motor oil), and high-tech industries (Italian holding “Finmeccanika” participates in the project “Sukhoi Superjet 100”; “Fiat” makes modern agricultural machinery, “Pirelli” has established in Russia production of tyres; Russian “Evraz” and “NLMK” are leading investors into the metallurgical sector of the Italian economy). At this, the share of Russian gas in Italy's imports makes more than 40 %, which makes the country quite dependent on Moscow not only economically but also politically.
Now the official Rome is concerned with negative effects of introduction of sanctions against Russia for the energy concern “Eni” (one of the shareholders of “South Stream”), as well as for the activities of the widely represented in the Russian bank “Uni Credit”. According to preliminary estimates, Italy may suffer losses from sanctions in the amount of more than 10 billion Euros.
Forecast. The spread of such negative economic trends, as a reduction in the index of industrial production, growth of unemployment by more than 12 %, preservation of low activity in the construction sector (-4.7 %), will be the major factors in the continuation of a technical recession in the country. According to preliminary estimates, the annual GDP growth of the country will make 0.1 %.
Localization of Italian business on solving domestic problems, combined with a high level of Russia's influence on the situation in the energy sector of Italy, determines the tendency for the official Rome's restraint of the position of the EU aimed at radical strengthening of pressure on the Kremlin.
2.4. Asia-Pacific Region
 Current trends. Ensuring the course of economic growth in the region is caused by the implementation of the following priorities for macroeconomic stabilization within the framework of national economic policy of regional leaders. At this, the ASEAN bloc shows a stable growth trend based on the preferences of intra-regional cooperation and deepening economic ties with neighboring countries. Growth of the concentration of direct foreign investments into the above-mentioned integration bloc is due to the favorable business climate and promising consumer market. At the same time as a result of the partial outflow of foreign capital in the Asia-Pacific region, begins to clearly stand out a group of outsider countries (Pakistan, Vietnam, and Thailand). Besides, the deepening of the Russian-Ukrainian crisis, and the continuing confrontation between China and United States and their military allies has become an additional factor of growing defense spending in Asian Pacific countries.
Current trends. Ensuring the course of economic growth in the region is caused by the implementation of the following priorities for macroeconomic stabilization within the framework of national economic policy of regional leaders. At this, the ASEAN bloc shows a stable growth trend based on the preferences of intra-regional cooperation and deepening economic ties with neighboring countries. Growth of the concentration of direct foreign investments into the above-mentioned integration bloc is due to the favorable business climate and promising consumer market. At the same time as a result of the partial outflow of foreign capital in the Asia-Pacific region, begins to clearly stand out a group of outsider countries (Pakistan, Vietnam, and Thailand). Besides, the deepening of the Russian-Ukrainian crisis, and the continuing confrontation between China and United States and their military allies has become an additional factor of growing defense spending in Asian Pacific countries.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. As part of the so-called “Eastern” direction of the economic policy (as a tool to counteract the economic isolation from the West), Russia is actively promoting in the APR countries and at the level of regional associations the idea of its readiness to give broad preferences for the sake of deepening trade, economic and investment cooperation with the states of the Asia-Pacific. Taking this into account, at an informal level, most countries in the region, which have export-oriented economic models with a large share of high-tech industries, do not exclude the possibility of using the consumer potential of the Russian market (to counteract the development of the crisis at national/ regional levels) in case of Western companies' leaving it.
However, the high potential for conflict in the Asia-Pacific region due to territorial disputes, as well as the expected strengthening of the PRC are the main constraints that will not help to change the previously stated positions on the Russian-Ukrainian conflict on the part of key regional players.
Forecast.
Direction of the development of Asian economies, as before, is critically dependent on investment and trading activity of the USA and EU. Countries of the region, including China, India and Indonesia, so far are using the necessary macro-financial tools to hedge risks from gradual reorientation of western investors to developed markets. Now stabilization policy of countries such as India and Indonesia is aimed at reducing the current account deficit. In its turn, China is implementing a set of measures aimed at minimizing the country's dependence on external exports and foreign investments.
Effective implementation of the reforms in the PRC can provide significant economic benefits to regional trading partners, exporting to China agricultural products, consumer goods and services and various services. On the other hand, the disordered recovery of economic balance in China may have a negative impact on regional and global growth, especially in countries that depend on exports of natural resources.
2. 4. 1. China
 Current trends of development. In the basis of the economic development of thePRC is the implementation of the concept of economic “rebalancing” (greater bias towards domestic consumption than towards the role of investments). According to the results of the 2nd quarter of 2014, the GDP growth made 7.5 %, due to successful monetary measures of the Central Bank of China (the devaluation of the Yuan by 2 %) and the balanced investment policy. In the economy of the country there are positive developments in the sphere of education, science and technology (the share of expenditure on innovative researches and developments has exceeded 2 % of the GDP). Infrastructure construction is forced, in particular early implementation of individual projects to supply regions of the country with water resources, expansion of the underground communications systems and other urban infrastructure facilities. The share of the central and western regions of the country in the national GDP continues to increase, which helps the harmonious regional development.
Current trends of development. In the basis of the economic development of thePRC is the implementation of the concept of economic “rebalancing” (greater bias towards domestic consumption than towards the role of investments). According to the results of the 2nd quarter of 2014, the GDP growth made 7.5 %, due to successful monetary measures of the Central Bank of China (the devaluation of the Yuan by 2 %) and the balanced investment policy. In the economy of the country there are positive developments in the sphere of education, science and technology (the share of expenditure on innovative researches and developments has exceeded 2 % of the GDP). Infrastructure construction is forced, in particular early implementation of individual projects to supply regions of the country with water resources, expansion of the underground communications systems and other urban infrastructure facilities. The share of the central and western regions of the country in the national GDP continues to increase, which helps the harmonious regional development.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. The Chinese side uses the escalation of the conflict around Ukraine in order to obtain tangible concessions in price for Russian energy carriers and increasing dependence of the Russian Federation on receiving credit and investment resources from the PRC. To balance the food security of the Russian Federation (as a result of blocking supplies from Europe) Chinese companies have already established centralized supply of food products to Russia. However, China's response to possible the Russian Federation's proposals (especially in the military and energy spheres) will be due to the fact that economic and technological importance of the West, in the context of furthering the declared official Beijing political guidelines and basic principles of development, is greater than Russia's energetic importance.
Consequences of China's reaching national priorities in the direction of Russia should become prospects of Beijing's getting major political preferences in the Asia-Pacific Region as a zone of its geopolitical influence. There is a high probability of China's intercepting the Russian Federation's strategic initiative in Central Asia and gaining control over the process of the expected change of political elites in the key countries of the region - Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan. An important strategic goal is to spread economic influence in the countries of South Asia with a view to occupy leading positions in counteracting the growth of India's regional ambitions.
Forecast. Macroeconomic orienting point of the course of the current government is to support GDP growth at 7.5 %, which is the best indicator within the framework of the government's economic policy for 2014-2015. Balanced index number of industrial production (9 % in July), along with activation of foreign investment resources (120 billion US dollars for the 2nd quarter of 2014) form the positive economic development of the country.
At the same time, due to the deterioration of the structure of the loan portfolio of the banking system of the country, have been recorded cases of corporate defaults, and their number is expected to grow due to the chain reaction, which will be monitored by government agencies. To counteract the crisis, has been intensified the struggle against the shadow lending and have been introduced restrictions on the creation of new enterprises with basic foreign capital, which is financed from international offshore funds. At the state level (regional limitations do not exist) have been supported mainly technology investments from Hong Kong, Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, Germany and the United States.
2.4.2. Japan
 Current trends of development. Japan's economy is in a phase of moderate stagnation. The main destabilizing factors of the economic equilibrium are the low activity of export-oriented sectors of the Japanese economy, combined with the slow recovery of domestic consumption (retail for July fell by 0.4 %). Since April 2014 has been recorded negative dynamics of the index of industrial production (as of July it is 3.1 %). After raising the consumption tax rate there is a significant decline in industrial orders and business activity in the engineering industry, which has a significant impact on the currency and stock markets of the country. Inconsistent adoption by the Government of important decisions relating to the energy sector and the role of nuclear energy in Japan, has led to some problems with the country's energy supply.
Current trends of development. Japan's economy is in a phase of moderate stagnation. The main destabilizing factors of the economic equilibrium are the low activity of export-oriented sectors of the Japanese economy, combined with the slow recovery of domestic consumption (retail for July fell by 0.4 %). Since April 2014 has been recorded negative dynamics of the index of industrial production (as of July it is 3.1 %). After raising the consumption tax rate there is a significant decline in industrial orders and business activity in the engineering industry, which has a significant impact on the currency and stock markets of the country. Inconsistent adoption by the Government of important decisions relating to the energy sector and the role of nuclear energy in Japan, has led to some problems with the country's energy supply.
At present, the Government of Japan's attention is focused on the development of a more effective formula for calculating corporate income tax (reduction of the basic tax rate due to the expansion of the tax base).
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. In the context of the crisis around Ukraine, the Japanese side adheres to a cautious line in resorting to the use of sanctions, due to the close trade and economic cooperation with Russia. Further destruction of relations with the Russian Federation could lead to significant economic losses, especially in the car industry (60 % of exports to Russia account for Japanese cars), and an increase in threats to energy security of the country (from Russia are transported 70 % of natural gas, up to 7 % of oil, 7 % of LNG and 6 % of coal). Also, the Japanese side may suffer losses due to the blocking of further implementation of investment projects into the RF’s energy sector, which apart from production, provides for development of infrastructure, processing and transportation.
Despite these risks, the official Tokyo within the framework of counteracting the Russian Federation's policy towards Ukraine is in constant dialogue with the United States, which encourages greater participation of the Japanese side in the programs of international assistance to maintain stability of the Ukrainian economy and to strengthen the economic isolation of the Kremlin. At this, Japan comes from the fact that the crisis over Ukraine is one of the major challenges for global markets. Economic cooperation with Ukraine will provide for assistance to stabilize its economy while refraining Japanese business from the policy of extended investments until the normalization of the situation in the state.
Forecast. Further preservation by the Central Bank of Japan of the inflation index at 3.6 % and initiation by S. Abe's government of stimulating economic reforms in terms of reducing the tax burden on business entities (it is planned to be reduced to the level of 20 %) will enhance the internal investment activity and attract venture capital investments into the national economy.
2.4.3. India
 Current trends of development. Stable current state of the Indian economy (GDP growth - 4.6 %) is leveled by its hyper-vulnerability to external destabilizing factors. The slowdown in its economic growth is due to both external and internal economic and social factors. The positive dynamics of the industrial production index since April 2014 (as of July - 3.4 %), along with effective measures to struggle against the unemployment (as of July - at the level of 5.2 %) forms a stable basis for deepening of economic reforms. In this context, N. Modi's government's main task is to restore high economic growth rate of 7-8 %. The stabilization course includes overcoming the negative trends of decrease in volumes of foreign investments, instability of the Indian rupee, the current level of food inflation, as well as accelerating pace of implementation of infrastructure projects.
Current trends of development. Stable current state of the Indian economy (GDP growth - 4.6 %) is leveled by its hyper-vulnerability to external destabilizing factors. The slowdown in its economic growth is due to both external and internal economic and social factors. The positive dynamics of the industrial production index since April 2014 (as of July - 3.4 %), along with effective measures to struggle against the unemployment (as of July - at the level of 5.2 %) forms a stable basis for deepening of economic reforms. In this context, N. Modi's government's main task is to restore high economic growth rate of 7-8 %. The stabilization course includes overcoming the negative trends of decrease in volumes of foreign investments, instability of the Indian rupee, the current level of food inflation, as well as accelerating pace of implementation of infrastructure projects.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. Significant cooperation dependence (especially in the military-industrial complex) on Russian technology creates the preconditions for a comprehensive blocking by the Indian side of the process of strengthening sanctions against the Russian Federation. Now the government of the country has declared a policy of greater international cooperation with Russia in the sphere of civilian nuclear energy programs, on directions of long-term lease of Russian submarines and joint production of a supersonic cruise missile “BrahMos”.
In general, the position of the official New Delhi on the development of relations with the RF will be determined by the current decline in the stability of the Indian economy to counteract external threats and challenges in the sphere of national security, primarily from China and some countries of South Asia, which are supported by the official Beijing (Pakistan, Sri Lanka). It is expected that the USA will be trying to more actively lobby its own interests in the Indian market - both, in the economic sphere and in the sphere of military-technical cooperation (with a focus on discrediting the cooperation with the Russian Federation).
Forecast. The revival in the Indian economy is expected after systemic reforms aimed at overcoming dependence on imports of crude oil, deficit of electrical power, solving problems of social security, facilitation of the processes of administrative decision-making. According to the World Bank and the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), India's economic growth in 2014 is forecasted to be at 4.7 %.
2.5. Near East
 The vast majority of countries in the region show growth in the non-oil sector, which is ensured by the involvement of state funds and the gradual recovery of the trend of growth in private lending. At the same time, due to the continuing instability in the region, countries-outsiders (Libya, Lebanon, Syria, Egypt, Iran) and leaders (Turkey, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates) are experiencing deepening of the crisis in the economy, the effect of which leads to a decrease in the level of competitiveness, employment, wages, consumer price inflation, decrease in tourist flows and foreign investments.
The vast majority of countries in the region show growth in the non-oil sector, which is ensured by the involvement of state funds and the gradual recovery of the trend of growth in private lending. At the same time, due to the continuing instability in the region, countries-outsiders (Libya, Lebanon, Syria, Egypt, Iran) and leaders (Turkey, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates) are experiencing deepening of the crisis in the economy, the effect of which leads to a decrease in the level of competitiveness, employment, wages, consumer price inflation, decrease in tourist flows and foreign investments.
Leading countries in the Near East and North Africa continue to implement measures aimed at further exemption from the traditional influence of Washington and Brussels, which is due to the weakening of the USA's positions and strengthening of the Russian ones in the region. This leads to the creation of new alliances that can offer an alternative vision of the western ways of resolving the crisis in the region. Thus, the emergence of the economic crisis in a number of regional countries causes the need to build both, new systems of values, as well as economic and political order of interaction between the major players.
In the context of the Russian-Ukrainian confrontation, Turkey is playing the most important role in the region. Thus, declaring the desire to ensure regional security and to prevent further provoking of political crises and spread of revolutions, Ankara condemns Moscow's occupation of the Crimea and the events in the East of Ukraine. At the same time, the energy dependence on Russia and the desire to obtain economic benefits keeps Turkey from joining the Western countries on the issue of economic sanctions against Russia. Besides, Ankara is seeking diplomatic and military-technical assistance from Moscow in the context of countering the regional instability belt around Turkey.
2.5.1. Turkey
 Current trends of development. Turkey's economy continues to demonstrate resistance to the crisis (GDP growth in the 1st quarter of 2014 was 4.3 %). This was not harmed even by the influence of the political instability as a result of the state's passage through the election cycle phase, which was completed in August by R. Erdogan's being elected the President. At the same time, the main problems remain the growing inflation (primarily due to a substantial increase in the cost of food and transport services) and high unemployment. At the same time in the country can be observed a high level of non-confidence in the banking sector, leading to a worsening of the quality of its assets. In this context, the Turkish authorities have introduced a number of restrictions on consumer loans and credit cards. Besides, against the backdrop of worsening of the economic conditions, Ministry of Finance has raised the added value tax, stamp duty, consumption tax, duties, official fines and commission fees.
Current trends of development. Turkey's economy continues to demonstrate resistance to the crisis (GDP growth in the 1st quarter of 2014 was 4.3 %). This was not harmed even by the influence of the political instability as a result of the state's passage through the election cycle phase, which was completed in August by R. Erdogan's being elected the President. At the same time, the main problems remain the growing inflation (primarily due to a substantial increase in the cost of food and transport services) and high unemployment. At the same time in the country can be observed a high level of non-confidence in the banking sector, leading to a worsening of the quality of its assets. In this context, the Turkish authorities have introduced a number of restrictions on consumer loans and credit cards. Besides, against the backdrop of worsening of the economic conditions, Ministry of Finance has raised the added value tax, stamp duty, consumption tax, duties, official fines and commission fees.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. Turkey's is cautiously reserved position towards the situation in Ukraine (although ensuring the rights of the Crimean Tatars is its priority). Ankara does not directly condemn Russia’s actions, due to the strategic nature of the Turkish-Russian economic cooperation, especially in the energy sphere. Besides, the sharpening crisis has a positive economic and financial effect for Turkey.
In particular, the use of economic sanctions against Russia by the USA and the EU has led to the trend of outflow from the financial and stock markets of the Russian Federation of foreign portfolio investments, lots of which have been sent to the Turkish market.
Also in Turkey can be noticed more active activity of Russian investors, who are studying the possibility of returning capitals to Western markets using Turkish financial intermediaries.
Given the high level of Turkey's dependence on foreign players in attracting foreign investments (USA, EU), ensuring energy security (RF), ensuring systemic transformations in the field of innovation and technological development (Western countries), MIC included, Ankara is trying to use the format of trade and economic cooperation with the Russian Federation (first of all through the preparation and conclusion of a bilateral preferential trade agreement on favorable conditions for Turkey) in order to obtain concessions from Brussels and Washington on the issue of Turkey's participation as a party in negotiations between the USA and EU on signing the Transatlantic Agreement on trade and investment cooperation.
The negative consequences of the Russian-Ukrainian conflict for the Turkish economy include high dependence on imports of iron, steel, wood, grain crops from Ukraine, as well as possibility of decrease in the budget revenues from tourism as a result of the lower flow of tourists from Ukraine and the Russian Federation.
Forecast. In the short term, one of the main risks for the Turkish economy will remain dependence on external and domestic lending. At the same time strengthening of the Turkish lira is a favorable factor for servicing external debts. In the second half of the year the Central Bank of Turkey expects continuation of disinflation (according to preliminary estimates it will reach 7.6-8.4 % in 2014) thanks to the increased domestic demand. Besides, the Ministry of Economy of Turkey forecasts further reduction in the current account deficit (at the end of the year less than 50 billion US dollars, amounting to 5.5 % of GDP) if export and employment indexes continue to improve.
In general, the adverse external economic factors have both a negative impact on the export-oriented model of the Turkish economy (the countries of the Middle East, North Africa, Ukraine and Russia account for a quarter of the Turkish exports) and positive effects (strengthening of the Turkish lira, increased stock market indices, reduction in the current account deficit).
2.6. Latin America
 Low rates of economic growth in LAC (Latin America and the Caribbean) countries are due to unfavorable conjunctural conditions in the world markets and a number of internal problems of individual countries, especially the largest economies in the Mercosur (Brazil, Argentina, and Venezuela). The socio-economic situation in these countries is characterized by low GDP growth, high inflation (in Argentina and Venezuela it is 10.9 % and 60.9 %, respectively), significant problems in the labor market, decrease in the foreign trade and inflow of investments. At the same time the greatest negative impact on the further development of the region caused the government of Argentina's (one of the three largest economies in the region) announcement of the technical default as a result of the country's inability to service its debt obligations.
Low rates of economic growth in LAC (Latin America and the Caribbean) countries are due to unfavorable conjunctural conditions in the world markets and a number of internal problems of individual countries, especially the largest economies in the Mercosur (Brazil, Argentina, and Venezuela). The socio-economic situation in these countries is characterized by low GDP growth, high inflation (in Argentina and Venezuela it is 10.9 % and 60.9 %, respectively), significant problems in the labor market, decrease in the foreign trade and inflow of investments. At the same time the greatest negative impact on the further development of the region caused the government of Argentina's (one of the three largest economies in the region) announcement of the technical default as a result of the country's inability to service its debt obligations.
At the same time, the situation in the countries of the Pacific Alliance (Mexico, Chile, Peru, Colombia) is characterized by a more dynamic economic growth, the average rates of which are 3.9 % by the results of the 2nd quarter of 2014.
The geopolitical struggle between the USA and China for influence in the region's economies, the search for new and transformation of old formats of interstate and interregional cooperation (BRICS, MINT, Pacific Alliance, IBSA triangle) will influence the development of the economic situation in the LAC region.
Russia (because of restrictions on imports of agricultural products from the West) is interested in supplies of pork, beef, poultry, dairy products, fruits and vegetables from Latin America. Besides, this year we can see increasing intensity of political and economic contacts between Russia and countries of Central and South America, with special emphasis on the development of cooperation with members of ALBA (Cuba, Venezuela, Bolivia, Ecuador, Nicaragua, Dominica, Antigua and Barbuda, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, and Saint Lucia). At this, the key principles of the development of Russia's relations with the countries of LAC are the military and military-technical cooperation, as well as investment and energy spheres.
2.6.1. Brazil
 Current trends of development. The Brazilian economy shows further deceleration in economic growth, which, according to the results of the 1st quarter of 2014 made 0.2 % as compared with the previous quarter. At the same time there is a reduction in the unemployment level to 4.9 %, inflation makes 6.5 %, the foreign trade turnover is growing.
Current trends of development. The Brazilian economy shows further deceleration in economic growth, which, according to the results of the 1st quarter of 2014 made 0.2 % as compared with the previous quarter. At the same time there is a reduction in the unemployment level to 4.9 %, inflation makes 6.5 %, the foreign trade turnover is growing.
Current processes that occur in the country's economy, show that the actions of the authorities to stimulate growth through government loans, consumer loans and financial support to the poor have exhausted themselves, and the country's leadership's s intention to develop the country's infrastructure, in particular to build new ports and other objects did not contribute to the growth of the economy.
Among the main negative trends in the economy of Brazil can be noted a low level of investment income, decrease in the demand on foreign markets, worsening of the financial state of large public companies, primarily of the oil-producing enterprise “Petrobras” (whose management has already announced a decrease in its investment program in 2014-2016 to 16 billion US dollars).
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. Current priorities of Brazil (as a strategic partner of Ukraine) determine its primary focus on providing in-depth format of cooperation with Russia. This policy of the country is due to the following:
- from the economic point of view, Moscow is a more important trading partner of Brazil (for the year 2013, the trade turnover with Russia amounted to 5.65 billion US dollars, which is more than 7 times higher than the same index in relations with Ukraine). Besides, in the situation when the country is in need of additional attraction of foreign direct investments, the Russian side in April 2014 expressed its being interested in investing into the program of development of the railway network and oil industry of Brazil;
- in preparation for signing of an action plan for trade and economic cooperation “Brazil-Russia” for 2014-2015, the official Moscow has expressed a desire to use the bilateral format of cooperation to ensure convergence (with the leading role of Brazil and Russia) of the association Mercosur and the Customs Union;
- taking into account the fact that the majority of the population perceives the change of power in Ukraine as a result of the direct influence of the United States, Brazil's President D. Rousseff's support of the official Kiev would mean approval of Washington's policy, which would lower her own rating before the presidential elections (in October 2014.).
Taking into consideration the format of close cooperation between Brazil and Russia, both at the bilateral level and within the framework of international organizations (in particular the BRICS and the UN), and both countries' compliance with anti-Western rhetoric in the international arena, appearing of disagreements between these countries over Ukraine is thought unlikely.
Forecast. It is expected that Brazil's economy will continue its slowdown. According to IMF forecasts, Brazil's economy in 2014 will grow by 1.8 %, and in 2015 - by 2.7 %. At the same time, the country's Central Bank expects a smaller increase in GDP - within 0.9 % and 1.5 %, respectively.
The main task of the leadership of Brazil is the need to take measures to stimulate the economy against the background of the approaching new electoral cycle (presidential elections in Brazil in October 2014). The authorities of the country in an effort to reflect advances in the improvement of social standards, de facto artificially constrain the growing influence of the crisis, leaving the taking of adequate anti-crisis measures for the post-election period. Despite the demonstration by Brazilian officials of optimism towards the future economic development of the state, in the government's economic policy so far there have not been made steps which could significantly accelerate the economic growth of the country. In turn, the limited available budgetary resources will continue to constrain the current government's financial capacity to fulfill its social obligations.
2.7. Africa
In African countries this year is expected acceleration of economic growth rates (expected - to 5.2 % in 2014). This is facilitated by the increased investments into the development of natural resources and infrastructure, the high level of spending. Besides, in the face of decline in the world prices for food and fuel, as well as thanks to a balanced monetary policy, inflation in the region has slowed. Today, a number of African countries are among the fastest growing economies in the world, which became possible thanks to circumspect macroeconomic reforms carried out in recent years, tremendous opportunities for trade, investments, entrepreneurship, research and introduction of new technologies, and tourism. Potential for economic growth in the region continues to be limited by the poor infrastructure and internal risks associated with social and political upheaval. An important task for African countries is to diversify exports.
2.7.1. The Republic of South Africa
 Current trends. The greatest influence on the economic growth rate have the following factors: the ongoing strikes, losing by key industries of competitive advantages in foreign markets, high level of inflation, depreciation of the national currency, a significant level of unemployment, social inequality. In particular, the latest strike affected the steel industry and mechanical engineering, which greatly influenced the automobile industry of the country. In this regard, foreign companies have suspended production of cars in South Africa, which reduced exports by 75 %. The above-mentioned in combination with strikes in the mining industry of precious metals leads to a decrease in industrial exports, which in turn increases the negative current account balance.
Current trends. The greatest influence on the economic growth rate have the following factors: the ongoing strikes, losing by key industries of competitive advantages in foreign markets, high level of inflation, depreciation of the national currency, a significant level of unemployment, social inequality. In particular, the latest strike affected the steel industry and mechanical engineering, which greatly influenced the automobile industry of the country. In this regard, foreign companies have suspended production of cars in South Africa, which reduced exports by 75 %. The above-mentioned in combination with strikes in the mining industry of precious metals leads to a decrease in industrial exports, which in turn increases the negative current account balance.
Risks associated with the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. Because of the weighty domestic political problems, the foreign policy to the leadership of the Republic of South Africa plays a minor role, but its main priority remains the development of diplomacy within the BRICS and multi-vector nature in international activities. For South Africa, the results of resolving of the Russian-Ukrainian crisis may have long-term consequences in foreign policy, and obtaining economic preferences in the nearest future.
Thus, the Russian side promises Pretoria to significantly increase investments into the metallurgical industry, production of raw materials, nuclear power industry, shipbuilding, high technologies and to deepen bilateral trade (in 2013 bilateral trade increased by 11 %, and in the first half of 2014 - by 10 % ). At the same time, the Russian Federation is ready before the end of the year to begin work on construction projects of 8 nuclear power units in South Africa and bring up for discussion the issue of their funding from Russia's state credit.
At the same time, deepening of cooperation and the Republic of South Africa's international support to Russia leads to worsening of relations with traditional partners in the USA and the EU, which can lead to blockage by the latter of volumes of financial assistance. Besides, Pretoria imports 90 % of wheat from Russia and Ukraine, which, given the sanctions imposed by the West against Moscow, will affect the pricing of raw materials from the Black Sea region.
Forecast. According to the results in 2014, is expected deceleration in South Africa's economic growth to 2 %. At the same time in the second half of the year, apart from external threats to the economy of South Africa, the state of the economy of the RSA will be affected by a number of potential internal risks. In particular, there are prospects of delay of implementation of infrastructure projects, first of all of putting into service of energy generating capacities (in the country there is still the practice of forced power outages during peak hours).
3. External risks and threats to the economic security of Ukraine
The influence of current trends of social and economic development of the world's leading economies on the dynamics of economic development of Ukraine in the situation of the Russian aggression suggests the possibility of growing risk of the following external threats:
- absence of factors of rapid growth in the European region and poor demand from the EU for imports of Ukrainian goods;
- partial slowdown in the USA's activity on the Ukrainian direction, due to the actualization for Washington of the issue of preventing violations of the current USA-China status quo in the Asia-Pacific Region;
- restrained perception by leading countries of the key for Ukraine's trade and economic interests regions (Middle East, South America, Southeast Asia, Africa) of the advisability of conceding interests in relations with the Russian Federation in favor of Ukraine;
- attempts of governments of developed countries to solve the problems of over-indebtedness (USA — 101 %, Japan — 22.7 %, Italy — 132 %, Belgium — 101 %, Singapore — 105 %, Greece — 175 %, Portugal — 129 %), which will restrict the flow of international investments;
- continuing the predominantly soft monetary policy both, in developed countries (the USA, Japan, Germany, France, UK, Canada), and in developing ones (China, Mexico, Turkey, Brazil, Indonesia), which will lead to growth of the risks of changes in the direction of flows of capital (return of capitals into the developed countries with their partial withdrawal from developing countries);
- rise of the role and influence of China's economy on global trade and investment flows.
In the context of further strengthening of sanctions pressure on the Russian Federation's economy, there is a risk that leaderships of some EU member states (in particular Cyprus, Hungary, Czech Republic, Finland, Italy) under the influence of political and business circles can change their attitude towards the possibility of additional sanctions against Russia.
 In any case, in 2014-2015 Ukraine's economy is up to a prolonged decline (technical recession), that will be followed by devaluation of the hryvnia and a sharp deterioration in consumer and investment sectors amid Russia's escalating aggression, in the economic sphere included. The most significant risk to Ukraine in the economic sphere is the Kremlin's taking measures to thwart the implementation of the anti-crisis program of the Ukrainian Government to destroy the foundations of the domestic economy.
In any case, in 2014-2015 Ukraine's economy is up to a prolonged decline (technical recession), that will be followed by devaluation of the hryvnia and a sharp deterioration in consumer and investment sectors amid Russia's escalating aggression, in the economic sphere included. The most significant risk to Ukraine in the economic sphere is the Kremlin's taking measures to thwart the implementation of the anti-crisis program of the Ukrainian Government to destroy the foundations of the domestic economy.
Future prospects will also depend on the ability of Ukraine to effectively use stabilization funds of international financial assistance, confirmation of which will be implementation of priority measures of the anti-crisis program in the first place on the management of public finances and real struggle against corruption.

